Table of Contents
What is ADHD?
Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder often diagnosed in childhood, though it can persist into adulthood. It is characterized by chronic inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. These symptoms can lead to significant difficulties in academic, work, and social environments, often creating challenges in relationships and day-to-day functioning.
How is ADHD Diagnosed?
Diagnosing Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder involves a comprehensive evaluation process led by qualified professionals. This may include several components:
– Clinical Interviews: Health providers will gather information from the individual suspected of having ADHD as well as from family members, teachers, or others who interact regularly with them.
– Behavioral Assessments: Psychologists often use standardized rating scales, such as the Conners’ Parent and Teacher Rating Scales, to objectively assess behaviors and symptoms.
– Direct Observation: This involves noting behaviors in different settings. ADHD symptoms can vary significantly based on the environment and the presence of various stimuli.
– Collateral Information: Gathering input from multiple sources provides a holistic perspective on the impact of the symptoms across different areas of life.
A structured approach ensures that the diagnosis is accurate, ruling out other potential causes of the observed behaviors.
Treatment for ADHD
The treatment of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder is multifaceted, often involving:
– Behavioral Therapy: Techniques such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can help patients develop strategies for managing symptomatic behaviors. Parent training and school interventions can also be beneficial.
– Medication: Stimulants (like methylphenidate and amphetamines) are the most commonly prescribed medications. However, non-stimulant medications such as atomoxetine and guanfacine may be appropriate for some individuals, particularly those with concerns about heart health.
– Psychoeducation: Facilitating understanding of ADHD for both the individual and their family is crucial. Learning about the disorder can empower individuals and families to seek appropriate interventions and create supportive environments.
– Supportive Therapies: This can include occupational therapy, which helps improve daily living skills, and counseling for emotional support.
How ADHD Affects Heart Health
Research is beginning to uncover links between Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder and cardiovascular health. Individuals with ADHD, especially those with untreated or poorly managed symptoms, may engage in behaviors that put their heart health at risk. These behaviors can include:
– Poor dietary choices: Impulsive eating patterns can lead to obesity and related cardiovascular risks.
– Sedentary lifestyle: Symptoms like hyperactivity may lead to a lack of engaged physical activity, contributing to heart health issues.
– Increased stress levels: The challenges of managing ADHD can lead to heightened stress, which negatively impacts heart health.
Additionally, hormonal changes and neurobiological factors associated with ADHD may contribute to cardiovascular implications, leading to a growing focus on how heart health should be monitored in individuals with ADHD.
ADHD Medications and Heart Health
Stimulant medications are effective in managing the symptoms of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder; however, they can also have cardiovascular side effects. Some potential effects include:
– Increased Heart Rate (Tachycardia): Stimulants can raise heart rate, which may be concerning for individuals with existing heart conditions or those predisposed to heart issues.
– Elevated Blood Pressure: Regular monitoring is essential as stimulants can cause transient increases in blood pressure.
Patients with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions require thorough evaluation and careful monitoring when starting stimulant medications. In such cases, healthcare providers may recommend starting with lower doses and conducting regular follow-ups to assess heart health.
Symptoms that Warrant a Visit to a Cardiologist
For individuals with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder on medication or those facing possible cardiovascular risk factors, it’s essential to be vigilant of signs indicating heart health issues. Some symptoms that should prompt a visit to a heart specialist include:
– Chest Pain or Discomfort: This can be a sign of various heart conditions.
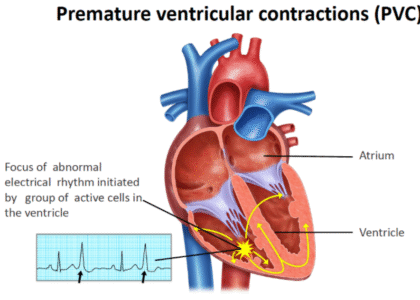
– Irregular Heartbeat or Palpitations: An awareness of changes in heart rhythm should not be ignored.
– Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing may indicate heart strain.
– Dizziness or Fainting Spells: These symptoms could signify inadequate blood flow.
– Unexplained Fatigue: Persistent tiredness that doesn’t correlate with other activities warrants further evaluation.
Testing Needed Before and During Treatment
Before initiating treatment, especially with stimulant medications, a thorough cardiovascular assessment is crucial:
– Comprehensive Physical Examination: This includes taking baseline measurements of heart rate and blood pressure, as well as reviewing any family history of heart disease.
– Electrocardiogram (ECG): An ECG measures the electrical activity of the heart and can reveal any underlying conditions that may warrant caution.
– Echocardiogram: Although not always necessary, it provides visual insights into heart structure and function for individuals at higher risk.
– Routine Monitoring: Regular follow-up appointments should be scheduled to monitor blood pressure and heart rate once treatment begins. Adjustments to medication may be required based on findings.
Conclusion
Living with ADHD does not solely involve managing symptoms related to attention and behavior; it’s also vital to prioritize cardiovascular health. The intricate relationship between ADHD, its treatments, and heart health underscores the importance of comprehensive care. Individuals with ADHD should keep an ongoing dialogue with healthcare providers regarding both mental and physical health to ensure they receive well-rounded support tailored to their unique needs. By recognizing symptoms early and maintaining vigilance over heart health, individuals with ADHD can lead healthier, more fulfilling lives.
Contact us at 406-272-2376 or schedule online.